Sand Casting
Sand casting refers to a casting method in which castings are produced in sand molds. It can be adapted to the production of castings in single pieces, batch production and mass production.
Certifications ISO 9001:2015 | CTQ Inspections | ISO 13485

What is sand casting?
The basic raw materials for making sand molds are foundry sand and sand binders. The most commonly used foundry sand is siliceous sand. When the high-temperature performance of silica sand cannot meet the application requirements, special sands such as zircon sand, chromite sand, and corundum sand are used.
In order to ensure that the finished sand molds and cores have a certain degree of strength and do not deform or get damaged during the handling, molding, and pouring of molten metal, it is generally necessary to add sand binders to bond the loose sand particles together to form the sand mold. The most widely used sand binder is clay; various drying oils or semi-drying oils, water-soluble silicates or phosphates, and various synthetic resins can also be used as sand binders.
Advantages of Sand Casting Process
-
Wear-resistant parts of sand-cast crushers are still very common in China, such as jaw plates, high-chromium hammers, crushing walls, and rolling mortar walls. Because in crusher equipment, as relatively large wear-resistant castings, their accuracy is relatively not high. Especially for the jaw opening, the finished product almost does not need to be polished by a lathe. Crushing walls, rolling mortar walls, roller skins, etc., only need to be polished by a lathe, which is particularly suitable for sand casting. Since sand casting is used for wear-resistant components such as jaw plates, high-chromium hammer heads, crushing walls, rolling mortar walls, and roller skins, these crushing equipment are more than 20% more durable than other products such as lost foam casting.
-
Sand casting is a kind of casting process. The molds used in sand casting generally consist of outer sand molds and cores. Because the molding materials used in sand casting are cheap and easy to obtain, and the mold making is simple, it can adapt to the single-piece production, batch production and mass production of castings. For a long time, it has been the basic process for casting production. At present, internationally, 60-70% of all castings are produced by sand molding, and about 70% of them are produced by clay sand molds.
-
Low cost
-
Simple production process
-
Short production cycle
-
Therefore, castings such as automobile engine blocks, cylinder heads, and crankshafts are all produced by the clay green sand process. When the green sand mold cannot meet the requirements, clay sand surface-dry sand molds, dry sand molds or other sand molds can be considered. The weight of castings made of clay green sand ranges from a few kilograms to dozens of kilograms, while the weight of castings made of dry clay can reach dozens of tons.
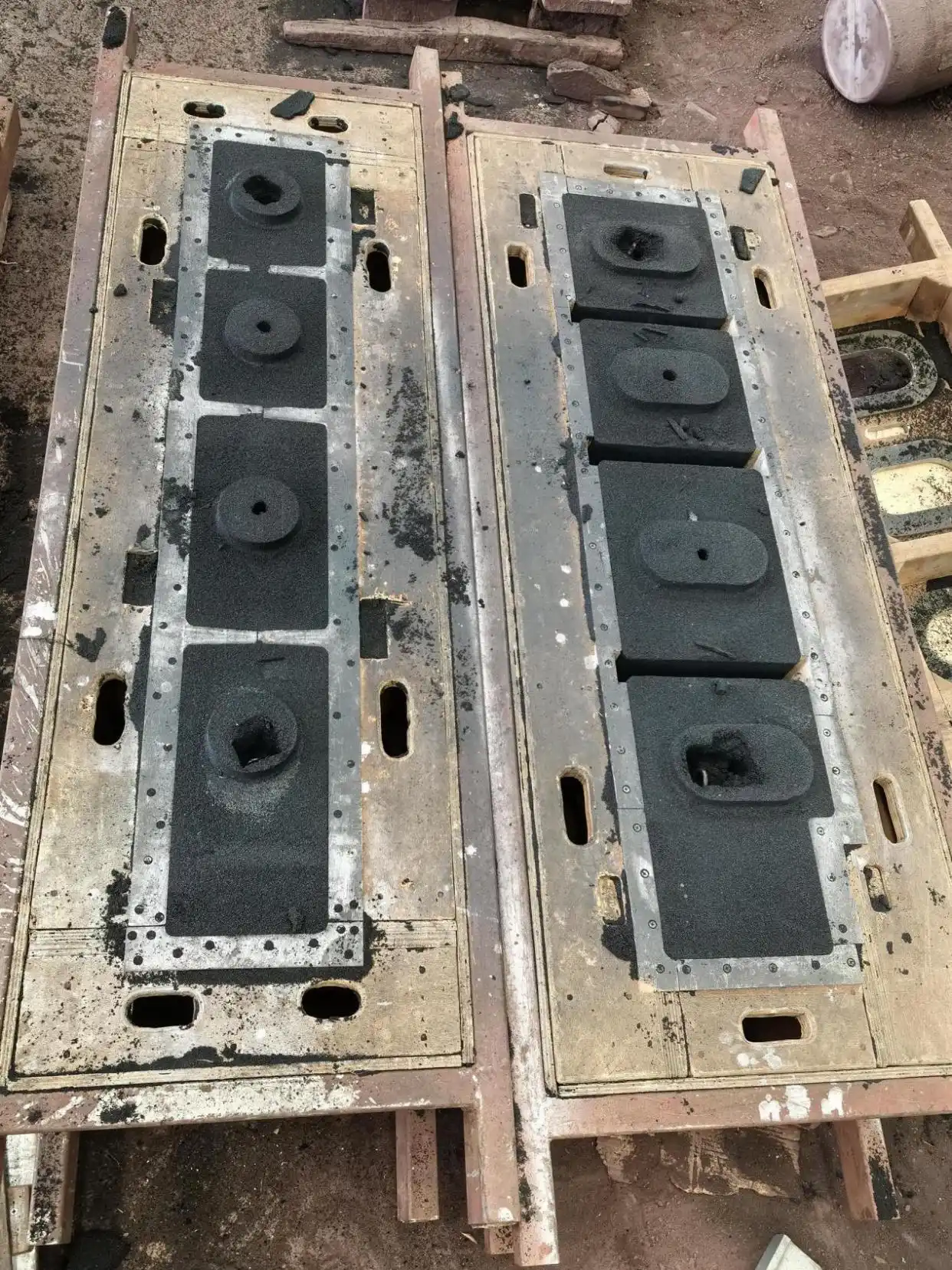

Sand Casting Production Process Flow
Sand Mixing Stage:
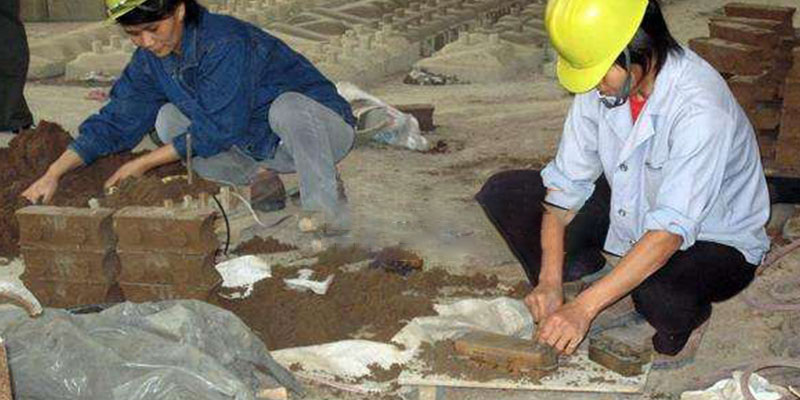
Prepare molding sand and core sand for casting. Typically, an old pattern and an appropriate amount of clay are mixed in a sand mixer.
Prepare molding sand and core sand for casting. Typically, an old pattern and an appropriate amount of clay are mixed in a sand mixer.
Mold Making Stage:
Create molds and core boxes according to part blueprints. Wooden molds are used for single-piece production, while plastic or metal molds (commonly called iron or steel molds) are used for mass production. Large castings may require pattern plates. Modern molds are primarily CNC-machined, significantly reducing production cycles (usually 2–10 days).
Create molds and core boxes according to part blueprints. Wooden molds are used for single-piece production, while plastic or metal molds (commonly called iron or steel molds) are used for mass production. Large castings may require pattern plates. Modern molds are primarily CNC-machined, significantly reducing production cycles (usually 2–10 days).
Modeling (Core Making) Stage:
- Modeling: Shape the casting cavity with molding sand.
- Core Making: Create internal features of the casting.
- Mold Assembly: Place cores into the cavity and close the upper and lower flasks.
This is a critical step in the casting process.
Melting Stage:
Match chemical compositions according to required metal specifications. Select a suitable furnace (e.g., cupola or electric arc furnace—cupolas are now mostly banned due to environmental regulations; electric furnaces are standard) to melt alloy materials into qualified molten metal (correct composition and temperature).
Match chemical compositions according to required metal specifications. Select a suitable furnace (e.g., cupola or electric arc furnace—cupolas are now mostly banned due to environmental regulations; electric furnaces are standard) to melt alloy materials into qualified molten metal (correct composition and temperature).
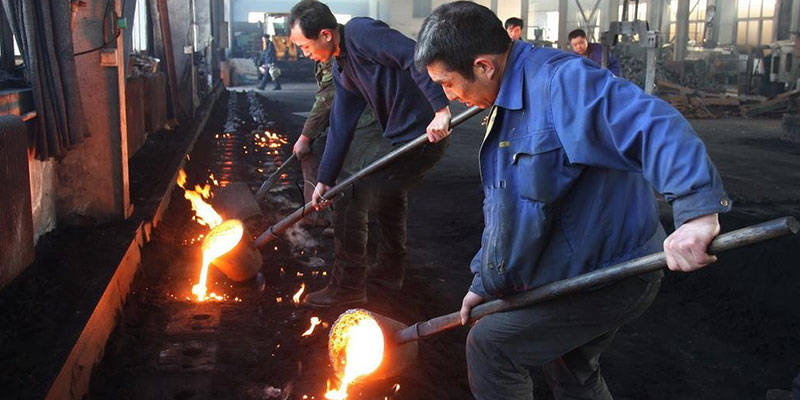
Pouring Stage:
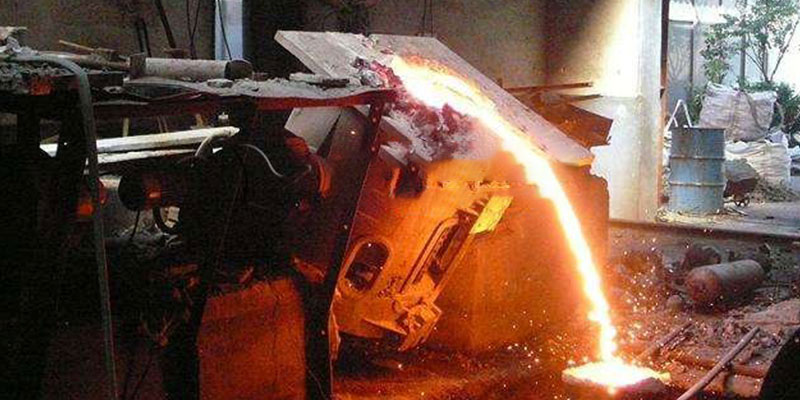
Transfer molten iron from the electric furnace into the mold using a ladle. Control pouring speed to ensure complete cavity filling. Note: Pouring is hazardous—strict safety protocols are required!
Transfer molten iron from the electric furnace into the mold using a ladle. Control pouring speed to ensure complete cavity filling. Note: Pouring is hazardous—strict safety protocols are required!
Cleaning Stage:
After solidification, remove the 浇口 (sprue) with hammers, shake off residual sand, and blast the casting with sand to achieve a clean surface. Castings meeting basic requirements are inspected and prepared for shipment.
After solidification, remove the 浇口 (sprue) with hammers, shake off residual sand, and blast the casting with sand to achieve a clean surface. Castings meeting basic requirements are inspected and prepared for shipment.
Casting Processing:
Castings with special requirements or defects undergo finishing, such as grinding or polishing with sanding wheels or grinders to remove burrs and ensure smooth surfaces.
Castings with special requirements or defects undergo finishing, such as grinding or polishing with sanding wheels or grinders to remove burrs and ensure smooth surfaces.
Casting Inspection:
Inspections occur during cleaning or processing to identify defects. Special requirements may necessitate additional checks.
Inspections occur during cleaning or processing to identify defects. Special requirements may necessitate additional checks.
Sand Casting Production
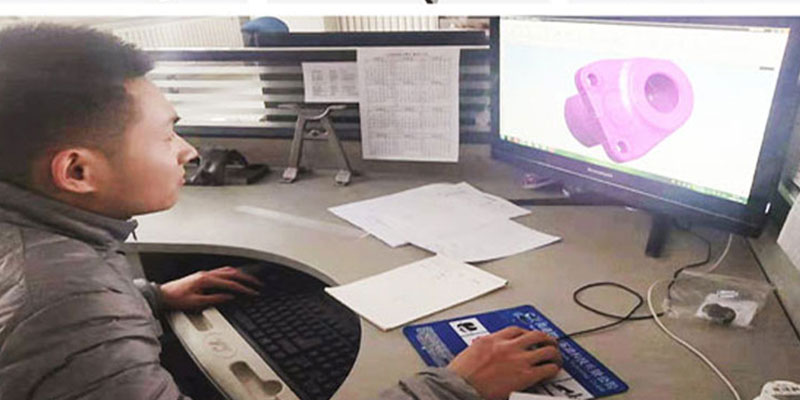

Mold development and design
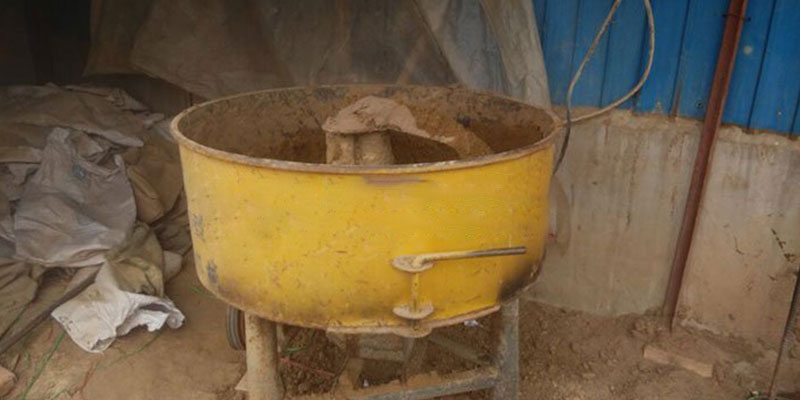

Sand mixing platform

Lost wax inspection

Wax assembly tree

Silica sol shell

Sodium silicate reinforcement

Steam dewaxing

Roasting and pouring
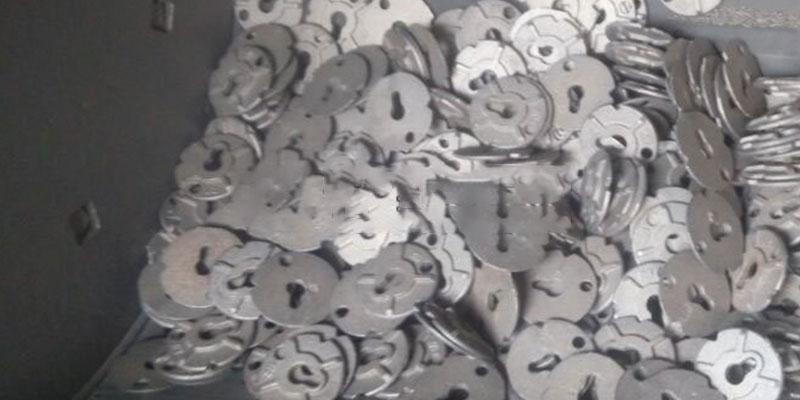

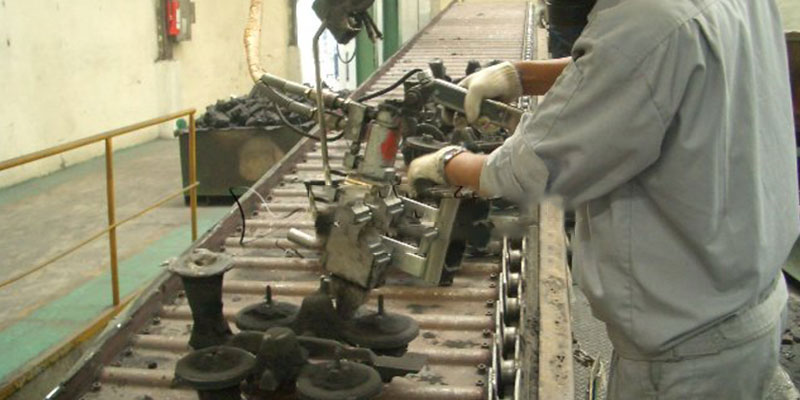
Sprue removal and grinding
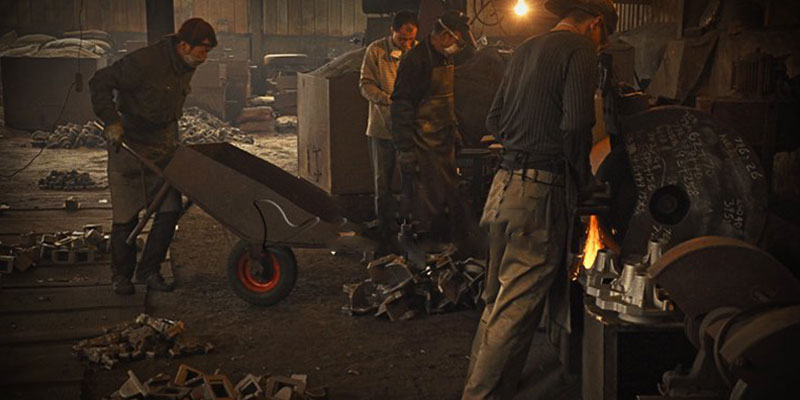

Post-processing
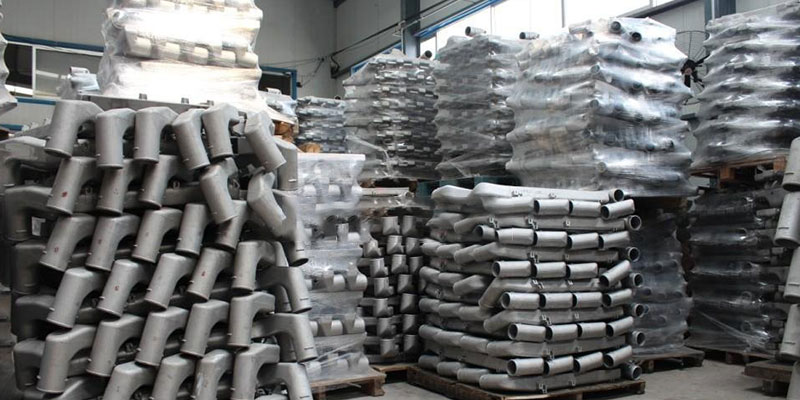

Complete precision castings
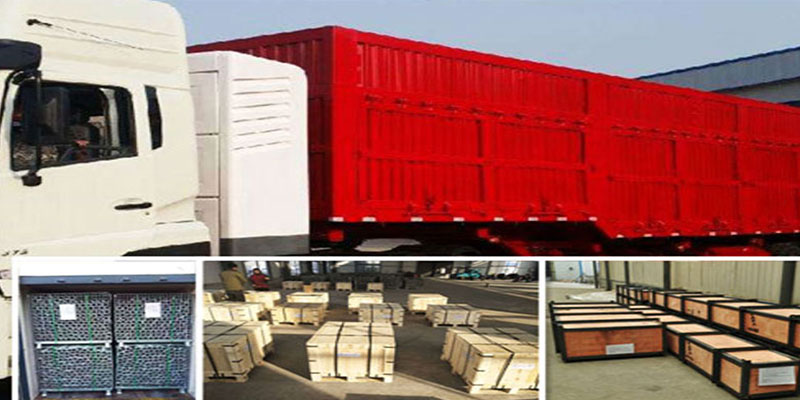

Packaging and transportation
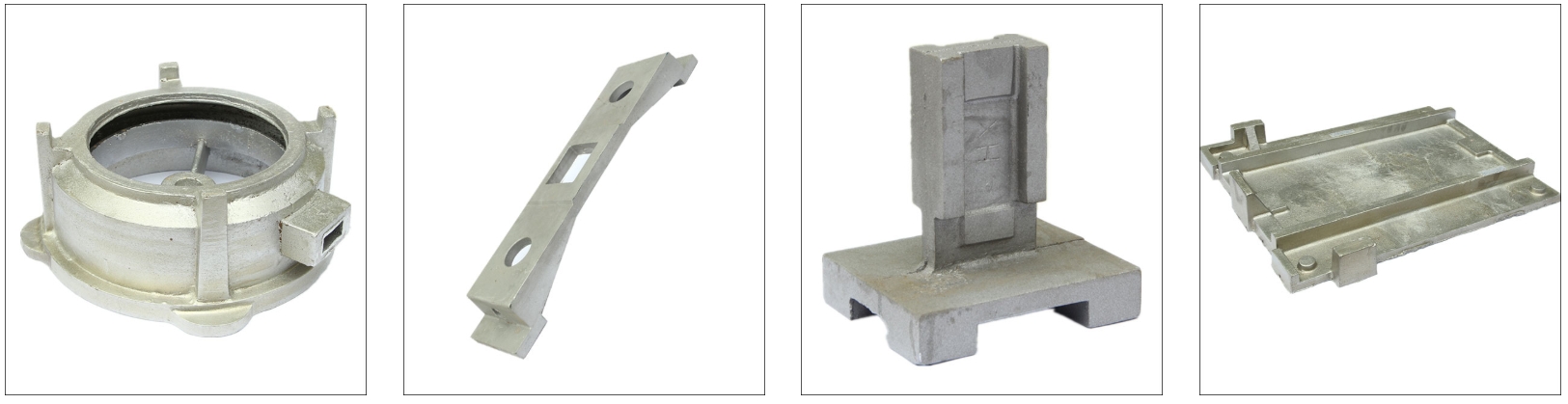
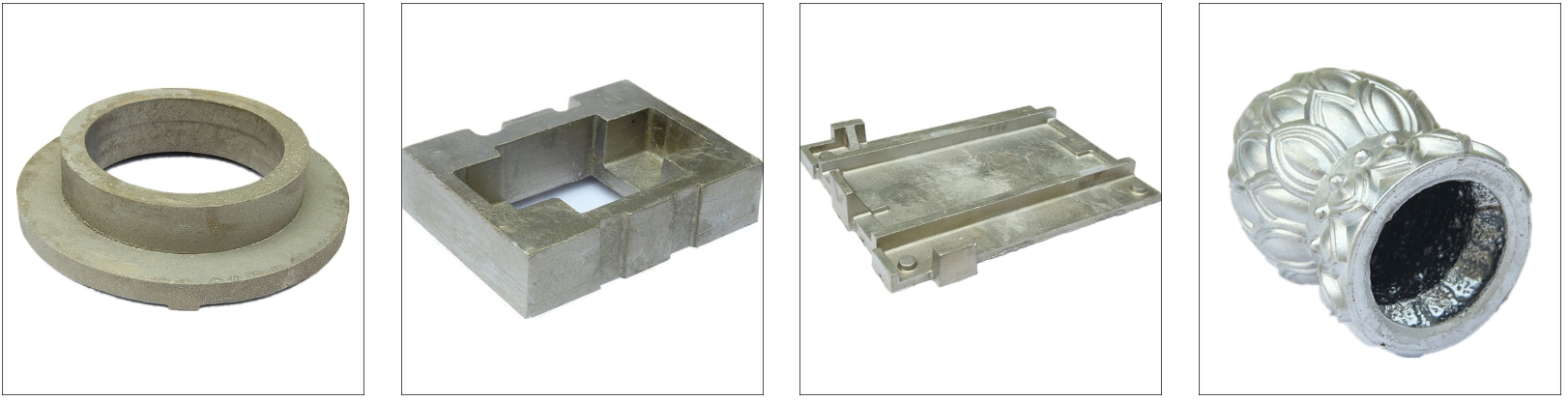
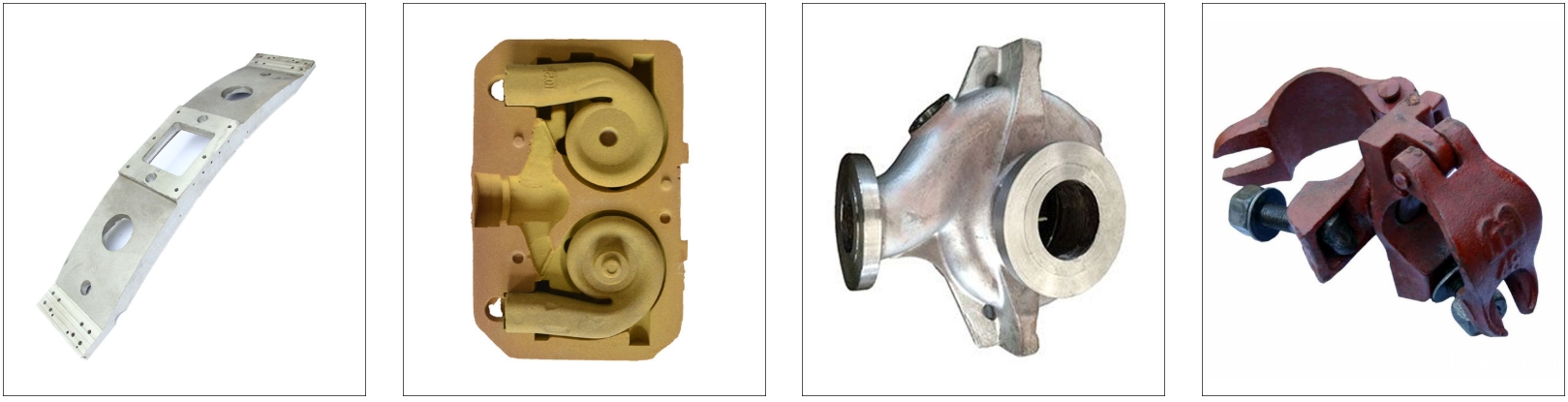
Sand Casting Cases
Manufacturing services can be applied to the actual design and small-batch production of die castings, sand castings, investment castings, metal castings, lost foam castings, etc.